What are HubSpot Lifecycle Stages, and How to Optimize?
Key Takeaways
-
A grasp of the HubSpot lifecycle stages enables teams to map customer journeys, personalize engagement, and boost marketing-sales alignment.
-
Lead nurturing with targeted content and smart scoring makes certain that contacts transition seamlessly and effectively from awareness to advocacy.
-
Customizing lifecycle stages is worth it if it fits your specific business processes better; don’t do it if it just introduces confusion and complexity.
-
Automation and ongoing rejection of stage movement can remove bottlenecks and streamline lead management, making transitions more efficient and swift.
-
Adding other properties such as lead status and deal stages, helps provide more insight into engagement and pipeline performance for better forecasting.
-
Quantifying stage conversion rates, funnel velocity, and revenue impact directs your continuous improvement efforts and keeps your business strategies aligned with your growth goals.
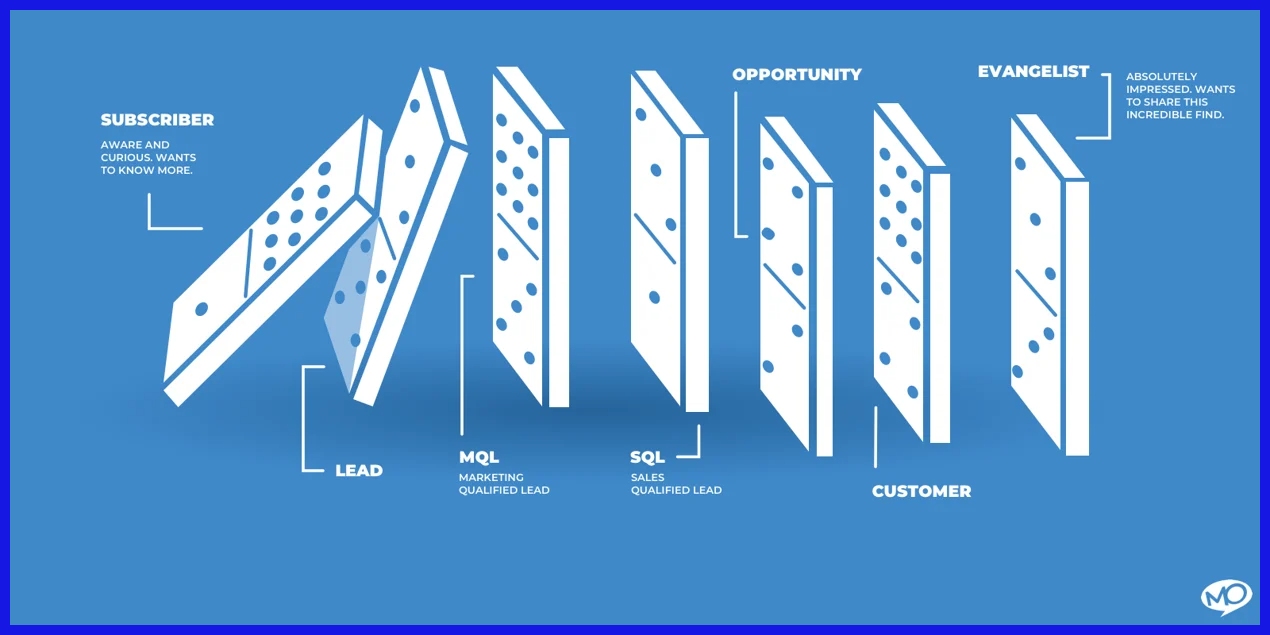
HubSpot lifecycle stages are the labels that track where a contact is in the sales/marketing process. Each stage—subscriber, lead, marketing qualified lead, sales qualified lead, opportunity, customer, and evangelist—allows teams to categorize and handle leads for improved follow-up.
I believe that using these lifecycle stages provides logical steps to walk your contacts from initial interest to long-term loyalty. The following sections analyze each stage and demonstrate how they function in practice.
What Are HubSpot Lifecycle Stages?
HubSpot lifecycle stages are a way to map out the path a contact or company takes as they transition from discovering your brand to becoming advocates. This system allows teams to track engagement, manage contacts, and measure the success of marketing efforts. Each stage represents a new level of engagement and interest, enabling companies to understand where each contact is in the buyer’s journey.
When used correctly, lifecycle stages enable teams to align marketing and sales, personalize outreach, and make data-backed decisions that increase conversion and retention.
1. Subscriber

Subscribers are contacts who’ve demonstrated basic interest by actively opting in to receive updates, newsletters, or other marketing content. They haven’t yet displayed a solid sales intent or engagement.
Content is key here. Consistent value, be it educational or exclusive insights, nurtures subscribers, builds trust, and warms them to your brand. This phase is all about staying top-of-mind with your brand without bombarding the contact with sales messages.
To push subscribers into the next stage, it’s clever to implement targeted calls-to-action in emails or on your website. Inviting them to webinars or to download a guide are good steps. Keeping the line open is key — regular communications that add value keep subscribers engaged and more likely to convert to leads.
2. Lead
Leads have advanced—they’ve made a move to express that they’re interested in your offering. It might be a form submission, a demo request, or an info request.
Qualifying leads is essential to ensuring time and resources are allocated to those most likely to convert. Lead scoring, which ranks prospects by engagement, behavior, or demographics, helps teams sift through and identify the highest potential contacts.
Targeted marketing campaigns, such as customized emails or remarketed advertisements, assist in pushing leads to the next step. By monitoring how leads engage with these initiatives, teams can fine-tune tactics to maintain engagement.
3. Marketing Qualified Lead

MQLs have met some criteria that indicate they’re ready for more direct marketing. This might be,
activity-based, such as regular site visits or heavy campaign engagement.
MQLs differentiate themselves from typical leads by demonstrating more interest. It makes the handoff to sales smoother and more efficient, as sales teams know these contacts are primed for outreach.
Custom content—case studies, product comparisons, or technical guides—nurtures MQLs and prepares them to engage with sales. This specificity can accelerate their transition to the next stage.
4. Sales Qualified Lead

Sales qualified leads, aka SQLs, are primed for sales outreach. They’ve exhibited intent, have a budget, and match your ICP.
Characteristics such as company size, role, and urgency are used to qualify SQLs. Sales teams can then leverage personal outreach, such as one-on-ones or personalized proposals, to convert these leads into opportunities.
Tracking SQLs lets us see what works and what doesn’t, so it’s easier to optimize the sales process. This increases conversions. Each step improves your chance of closing.
5. Opportunity
An opportunity is a qualified prospect engaged in interest. Sales teams are working these contacts, frequently with proposals or negotiations.
Opportunities in the pipeline are essential for forecasting and resource planning. Timely follow-ups – calls, emails, or meetings – make a big difference.
Researching data from previous opportunities aids teams in identifying trends, optimizing their sales playbook, and enhancing win percentages.
6. Customer

Customers have bought. They’re not just a transaction; they’re a relationship to nurture.
Continued engagement — onboarding, support, and check-ins, etc. — keeps them happy and reduces churn. To drive more value, implement strategies like loyalty programs or exclusive offers for repeat purchases.
Listening to customers makes for smarter products and services.
7. Evangelist
Evangelists are those customers who take it upon themselves to be an advocate for your brand. They post reviews, send referrals, and increase your status.
Referral and testimonial encouragement via easy programs rewards this loyalty. Evangelists’ feedback helps identify strengths and weaknesses.
Evangelists are valuable. Keep them engaged and recognized.
Why Lifecycle Stages Matter
Lifecycle stages provide an organized means to monitor and evaluate your customers’ journey. They enable teams to identify key junctures, maximize engagement, and translate the insight into marketing and sales strategies. By mapping out these stages, businesses can notice trends, conversion rates, and ways to grow.

Definitive lifecycle stages assist in tearing down walls between teams. When all employees operate under the same definitions for leads, opportunities, and customers, it becomes simpler to align strategies. Teams collaborate on focused workflows, such as routing sales-qualified leads or nurturing cold leads with marketing.
This alignment accelerates decision-making and keeps teams focused on common objectives.
Enhance Personalization
By understanding where each contact is in the lifecycle, teams can craft messages that seem specific and timely. An awareness stage lead might get useful blog posts, whereas a purchase stage lead gets a product demo offer. By segmenting audiences by stage, campaigns are hitting the right people with the right content, increasing the likelihood of engagement.
Data-driven insights from lifecycle tracking simplify seeing what resonates with various groups. Teams can track open rates and click-throughs, then adjust messages to accommodate shifting demands. If a contact converts from a lead to a sales-qualified lead, the content they receive should change to reflect their interest and readiness.
This feedback loop of adjustment keeps communication germane.
Conversion events in digital campaigns based on lifecycle stages provide teams with real-time data to plan better. This aids in both short-term goals and long-term expansion.
Track Engagement
Lifecycle stages allow teams to observe which channels and messages are most effective at each point. They indicate whether blog posts, ads or landing pages nudge people to the next stage. Following this flow helps direct content strategy and resource distribution.
It emphasizes drop-off points, so teams can repair weak areas quickly. Having clear stage criteria keeps reporting honest.
Customizing Your Stages
HubSpot lifecycle stages help you track where contacts and companies sit in your sales and marketing process. Defaults suit a lot, but not all, business models. Customizing these stages can help match your specific buyer journey and align with team workflows, resulting in clearer reporting.
When to Customize
Modify the stages when your process doesn’t match HubSpot’s defaults. If you have a custom customer journey – e.g., Software subscription with trial and onboarding – you may need additional stages to represent those steps.
In other words, adding a “lost” stage, for instance, can assist in keeping your customer count accurate by pushing churned users out of the active bucket. Hear the team out. Teams typically notice holes or confusion in the default configuration.
If reports feel off, or if tracking doesn’t represent real progress, that’s an indication your lifecycle stages require a revisit! Customizing is handy if you need enhanced reporting or want to align stages to internal handoffs, such as when sales hands leads off to customer success.
When to Avoid
Don’t mess with it if the default works for you. Over-customizing–too many stages or changes without analysis–can be confusing. If your team already finds the existing stages clear and helpful, don’t add any more.
Complex or ambiguous customization makes adoption difficult. If changes confuse team members or stakeholders, default. Be sure to verify that your modifications will aid all members in tracking the status of contacts.
This is particularly crucial for international teams or non-English settings, since customizations might affect translations or integrations.
Implementation Steps
Start with clear steps: define why you need new stages, map out the buyer’s journey, and name each stage for easy recognition. In HubSpot, drag and drop stages using the ten dot group to the left of the stage name.
Don’t do anything too complicated–smallish hacks are usually best. Once you’ve updated, train your team on the new names and flow. Define What Your Stages Mean Be sure everyone understands what the stages signify.
Onboard using documents and reference guides to bypass confusion. Keep an eye on the fresh configuration as time passes, and observe whether tracking and reporting get better. If moving a contact backward, clear the old value before setting the new. Make sure to always record these modifications in your CRM for reference.
Key Considerations
Customizing lifecycle stages doesn’t have to be difficult. The objective is improved tracking, not additional clutter. Lifecycle stage is a categorization, not a state—use lead status for more granular updates.
Review your stages periodically to keep them consistent with your evolving business and customer journey.
Optimizing Stage Progression
Optimizing HubSpot lifecycle stage progression refers to molding every stage to fit your company’s sales process and customer journey. It promotes collaboration and enables customers to self-serve, always. It begins with a definitive progression from Subscriber to Lead to MQL to SQL to Opportunity to Customer to Evangelist.
By transforming these stages and maintaining their synchrony, companies circumvent headaches like Salesforce’s bad syncing or broken picklists from misapplied rules. Periodical checks and tweaks make stages conform to actual sales activity. Departments have to be in sync, as transparent collaboration makes certain lifecycle stages are applied correctly and achieve optimal performance.
Strategic Nurturing

Each lifecycle stage requires a separate nurturing plan. For Subscribers and early Leads, light, informative content like welcome emails or brief blog digests is designed to build trust but not overload. As contacts become MQLs or SQLs, campaigns have to get more refined and focused, providing webinars, demos, or comparison guides that respond to inquiries regarding your services.
Engagement tracking counts, always. Open rates or clicks are great for revealing whether an email series is effective or whether contacts are falling away. With this information, teams can fine-tune messages or send new offers that more closely align with the stage. Your ambition should be to get people further along, not just to stay in contact.
For instance, if leads dismiss webinar invites, a quick case study might perform better. In global teams, distributing performance data allows you to learn fast and make adjustments for local needs.
Intelligent Scoring
Scoring tells teams which leads to pay attention to. It begins with easy heuristics—such as awarding points for email opens or site visits—and becomes more sophisticated as you learn from previous deals. For instance, if previous customers tend to download a guide prior to purchase, score that action a little higher.
Scoring models require adjustment. If the market changes or a product launches, the criteria have to change. Teams ought to revisit closed deals every few months and determine if the scores align with who purchased or became a long-term customer.
That way, scoring captures what’s going on, not just what’s routine. Armed with good scoring, sales teams know who’s ready now and who needs more time. This keeps resources targeted where they count, accelerating the sales cycle and reducing wasted effort.
Seamless Automation
Automation takes care of stage moves in the background. For instance, if a contact completes a demo request, an automated workflow can switch their stage from MQL to SQL, notify sales, and initiate a personalized email sequence.
These actions should be easy and beneficial. Too much automation can baffle contacts or teams, so it’s smart to leverage evident triggers, such as certain form completions or engagement levels. To each workflow, checks should be baked in. If contacts stall or don’t respond, the flow can pivot or notify a staff member.
Monitoring automation metrics, such as the number of leads that progress from SQL to Opportunity in a given month, aids in identifying bottlenecks. Teams can then tweak stages or introduce more self-service tools, such as FAQs or video walk-throughs, to maintain prospect momentum.
Ongoing Review
Review stages frequently. Correct sync or rule violations. Optimize stage progression as the business matures. Keep the teamwork tight.
Beyond the Default Properties
HubSpot’s default lifecycle stages are useful, but most companies outgrow them. Custom properties and extra fields allow teams to capture information that aligns with their specific workflows — for example, customer preferences, industry, or source of engagement. They provide these additional layers to follow customer activity across multiple platforms, enhance data qualit,y and enable more effective outreach.
Custom stages such as “Inactive Lead” or “Lost Opportunity” assist with handling contacts that fall outside the normal stages.
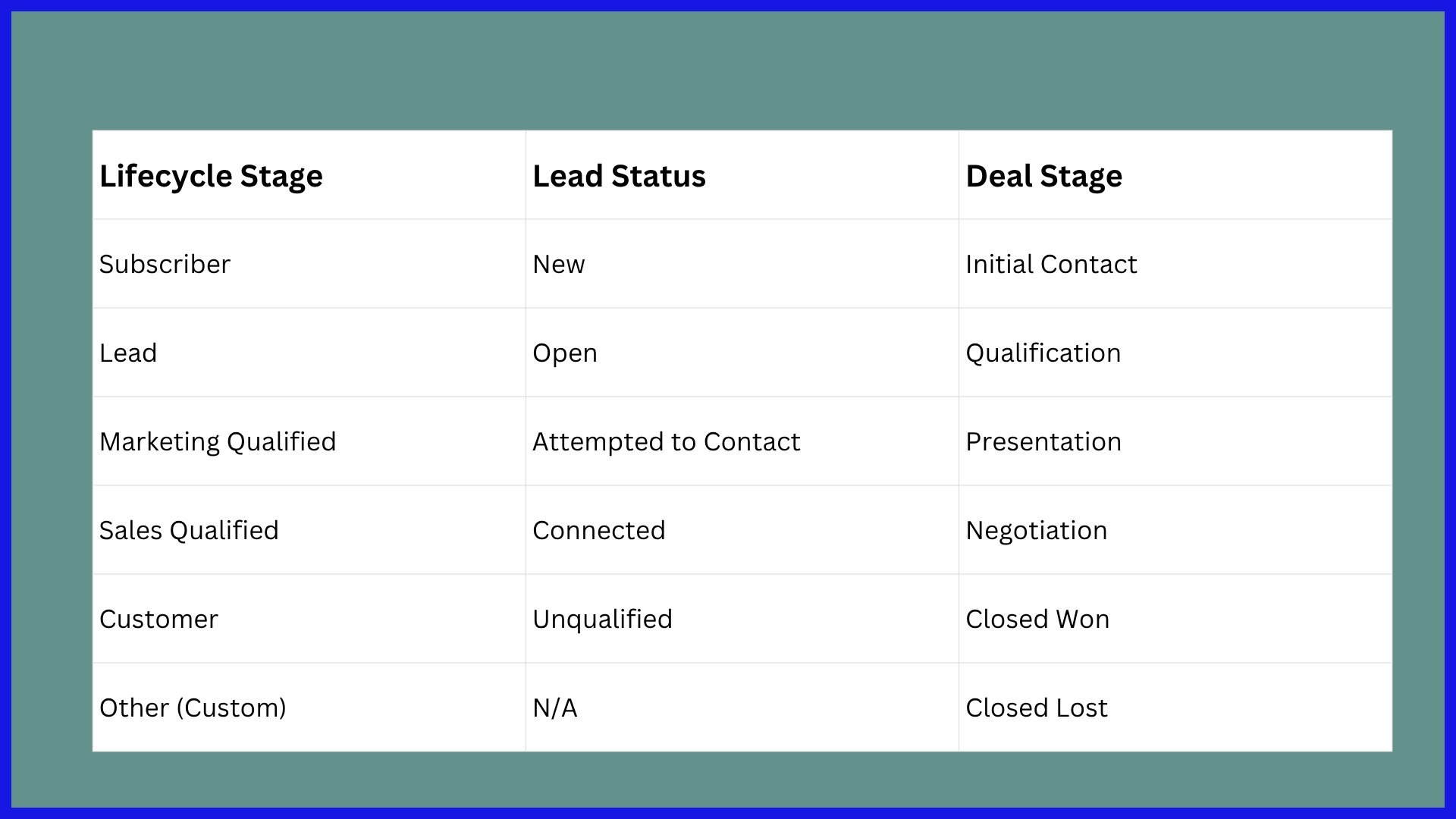
Lead Status
Lead status properties separate leads by active status – for instance, “New,” “Open,” or “Unqualified.” This helps simplify viewing who’s engaged, who needs follow-up, and who may need a different strategy.
Lead status serves teams for more than simply segmenting contacts. It helps sales and marketing to contour their outreach. So, if a lead is listed as “Attempted to Contact,” for instance, the marketing team could run a specific campaign to reengage.
It assists salespeople in identifying who’s prepared for a call and who requires additional time. Maintaining accurate lead status updates keeps your records fresh and reliable. Stale lead statuses result in lost opportunities or wasted energy.
Lead status data over time can reveal trends, such as which statuses typically lead to deals or where prospects fall off. This knowledge allows squads to customize communication for improved performance.
Deal Stages
Deal stages indicate where a sales opportunity is, from “Initial Contact” to “Closed Won” or “Closed Lost.” Defined deal stages let teams track actual sales momentum, not just a list of names.
Establishing stages assists with forecasting sales and managing the pipeline. Sales managers can identify languishing deals or bottlenecks. They can make more precise revenue projections.
Getting deals through stages is simpler when it’s transparent. For instance, after a demo call, advancing a deal from “Presentation” to “Negotiation” is an easy update anyone on the team can view.
Monitoring the transfer of deals among stages provides an understanding of what is effective. If deals keep stalling at a certain point, this might be an indicator that more training or an approach change is needed.
Teams can leverage this information to optimize their strategies and increase win rates.
A Cohesive System
Everyone on the team should understand how lifecycle, lead, and deal properties connect. Leveraging a centralized CRM is critical for this.
This way, teams can monitor every piece of customer interaction under one roof. Taking a step back to review the system frequently helps identify missing gaps and ways of working faster.
Teams can utilize custom properties to integrate with other tools, like marketing platforms or service software.
How to Measure Success
How to measure success with HubSpot lifecycle stages depends on how effectively you track and analyze each step in the customer journey. Measurement allows you to see where leads are dropping off and where your strategies are finding traction.
With transparent KPIs and analytics, you can continue refining your marketing and sales.
Stage Conversion Rates
|
Lifecycle Stage |
Conversion Rate (%) |
|---|---|
|
Subscriber |
18 |
|
Lead |
12 |
|
MQL |
9 |
|
SQL |
6 |
|
Opportunity |
4 |
|
Customer |
2 |
|
Evangelist |
1 |
Low conversion rates between stages, such as MQL to SQ,L can indicate a need for closer marketing-sales alignment. For instance, if your SQL rate is low, you might need to revamp your lead scoring criteria or sales follow-up process.
Measuring conversion rates over time with automated tools provides a clear indicationof whether changes are yielding improved results.
Funnel Velocity
Funnel velocity measures the average amount of time leads spend in each lifecycle stage. Fast movement indicates your sales process is slick, and slow movement can identify a bottleneck.
For example, if leads are spending too long at the MQL stage, perhaps your content isn’t compelling enough, or the hand-off to sales is sluggish.
To accelerate funnel velocity, identify stages where leads loiter. Experiment with targeted emails or ad campaign tweaking or more relevant content.
Utilize your funnel velocity data to identify trends and keep your team’s attention on accelerating sluggish stages. This not only helps your sales team close deals faster, it keeps the pipeline healthy.
Revenue Impact
Measuring revenue impact is more about seeing how effectively each lifecycle stage converts to sales. For instance, measure how many SQLs convert to customers, and which marketing channels generate the highest revenue.
This allows you to spend the channels that perform best as well. Keep your sales and marketing efforts on track with a regular review of revenue data.
If a lot of revenue comes from a small set of leads or campaigns, move your budget and time there. Revenue impact lets you observe whether stages such as “Evangelist” are generating referrals or repeat purchases, demonstrating long-term value.
Continuous Improvement
Establish reporting periods to review all KPIs. More accurately, use tools that allow you to track lifecycle changes automatically.
Be sure to constantly refresh your strategies based on what is and isn’t working. Customize lifecycle stages to fit your specific sales process.
This makes tracking more significant and allows you to identify holes or victories immediately.
Conclusion
HubSpot lifecycle stages give your team a clear, structured way to monitor where leads and customers are in their journey. When mapped and used correctly, they surface gaps, highlight friction, and guide next steps — whether that’s timely follow-ups or smarter handoffs between sales and support.
Imagine a demo request with no follow-up — that gap is more than a missed opportunity; it’s a signal. Or a happy customer who upgrades after proactive check-ins — that’s lifecycle strategy in motion.
To maximize HubSpot, verify your setup, regularly review each stage, and align your team around shared visibility.
Want to go deeper? KPI.me can help you visualize, benchmark, and optimize your lifecycle stages in real time — so you’re not just tracking progress, you’re accelerating it.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are HubSpot lifecycle stages?
HubSpot lifecycle stages are buckets that categorize where a contact is in your marketing and sales funnel. They assist teams in handling and cultivating leads, prospects, and customers.
Why should I use lifecycle stages in HubSpot?
Lifecycle stages help you segment contacts, customize messages, and rank leads. Which increases conversion rates and builds customer loyalty.
Can I customize lifecycle stages in HubSpot?
Yes, you can customize lifecycle stages for your business process. By custom stages, you can fit HubSpot to your own sales and marketing processes.
How do I move contacts between lifecycle stages?
You are able to shift contacts manually or create automated workflows in HubSpot. Make sure contacts move forward as they interact with your brand.
What metrics help measure lifecycle stage success?
Important KPIs are stage conversion rates, time in a stage, and total leads to customer conversion. Monitoring these identifies bottlenecks and hones your strategy.
Is it possible to use properties beyond the default lifecycle stages?
Yes, you can create custom properties in HubSpot. These offer more in-depth insights and assist in tracking extra information unique to your business.
How do lifecycle stages benefit sales and marketing alignment?
Lifecycle stages create a clear structure for both teams. They get everyone on the same page about a contact’s path, creating more alignment and increased efficiency.